
- Presenters:
- Stacia Van Zetten
- Duration:
- 45 Minutes
- Format:
- Audio and Video
- License:
- Short Description:
- The general sentiment around construction and modern technology is that the industry has been slow to embrace it. While this is true of the past, the current and future construction industry is all about modern technology. Not only does technology help to make the industry safer (something that has been a struggle for a very long time), but it is helping contractors to take back control of their budgets, to make smarter choices about project planning and equipment and is, consequently, pushing the green-construction trend forward. The purpose of this presentation is to provide a summary on the current technologies being used in the construction industry with a focus on concrete and to dig even further as to how these can be applied to repair projects. It will provide case studies on how using technology to bring ambient and concrete temperature, relative humidity and strength (among other) data online can help contractors be more efficient.
- Price:
- $15.00 - $25.00

- Presenters:
- Hamed Layssi
- Duration:
- 45 Minutes
- Format:
- Audio and Video
- License:
- Short Description:
- The application of nondestructive testing and evaluation for detecting existing defects and anomalies in concrete structures will be presented. Proper inspection and assessment is an integral part of a successful repair and rehabilitation. A well-defined inspection will help asset owners and their consultants in identifying the location and extent of existing defects, and enabling them in selecting proper repair materials and optimizing the area that needs rehabilitation. Moreover, NDT methods can help identify potential defects that are not visible to the naked eye, such as early-stage delamination, corrosion, and other durability related issues. In this presentation, several cases in Canada will be demonstrated, where the results of nondestructive testing and evaluation have been used to help consultants and contractors with cost-effective and reliable repair planning. Applications of ground penetrating radar, ultrasonic pulse echo tomography, seismic tomography, will be discussed.
- Price:
- $15.00 - $25.00

- Presenters:
- Erik Villari | Michael Salera
- Duration:
- 45 Minutes
- Format:
- Audio and Video
- License:
- Short Description:
- Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles and Systems (aka UAVs aka Drones) continues to be a hot topic for engineers and designers. Within the past 10 years, we have seen technology change how we live, work, play and learn. These advances in technology have enabled humans to be more efficient as well as socially and environmentally conscious and connected. Advances in engineering technology and efficiency have expanded structural engineer’s roles in inspection services. This presentation will highlight drone utilization for exterior surveys and inspection, impact on the built environment, and how drones will continue to influence in the future. This includes areas that are too dangerous for humans or structures where rigging can be difficult or impossible as well as the cost benefits of using a drone. The presentation will also delve into the effectiveness and appropriate applications of drone usage, specifically for hands-on applications.
- Price:
- $15.00 - $25.00

- Bundle:
- Fall Conference Bundle
- Presenters:
- Billy D. James, P.E.
- Duration:
- 22 Minutes
- Format:
- Audio and Video
- License:
- Access for 6 month(s) after purchase.
- Short Description:
- Post-tensioned concrete is a strong and durable material for construction of exposed parking structures. These types of structures are also fire resistant, but they can be damaged depending upon the severity of the fire. The structure in this presentation suffered significant fire damage early in its construction. The presentation will cover the discovery and testing methods used to determine the extent of fire damage, and the design of the repairs that were instituted to restore strength and allow construction to continue.
- Price:
- $15.00 - $25.00

- Presenters:
- Mike Tracy
- Duration:
- 43 Minutes
- Format:
- Audio and Video
- License:
- Access for 6 month(s) after purchase.
- Short Description:
- Increasingly, the Construction Industry is being dramatically impacted globally by internal and external forces. These influences range from acute labor and skill shortages, demographic and urbanization shifts, as well as, the Industry’s conversion from analog-based processes to digital workflows. This presentation will overview ten significant trends which are uniquely affecting the Construction Industry, creating both new challenges and opportunities, while transforming the Construction Industry.
- Price:
- $15.00 - $25.00

- Bundle:
- Fall Conference Bundle
- Presenters:
- Anirudh Goel | Mr Charles Hammond
- Duration:
- 28 Minutes
- Format:
- Audio and Video
- License:
- Access for 6 month(s) after purchase.
- Short Description:
- The presentation, through case studies, talks about emergency response services for structural issues encountered during construction of new design projects. Among other examples is an eleven story precast parking structure. The contractor observed significant diagonal faulted cracking of L-beams (supporting double-tee sections) near bearing locations, few days after pouring topping slab. In addition, inverted-tee girders were observed to be supported on cracked corbels at other locations. A quick turn around was required to mitigate any immediate life safety hazard posed by the structural distresses and buy time for thorough investigation, non-destructive testing, analyses, and repair design. Another example is a seven story precast parking structure. The structure was under construction and reportedly erected out of plumb. Poor concrete placing practices and poor weld detailing led to widespread cracking in multiple structural elements throughout the structure...
- Price:
- $15.00 - $25.00
- Bundle:
- Fall Conference Bundle
- Presenters:
- Scott M. Greenhaus
- Duration:
- 1 hour
- Format:
- Audio and Video
- License:
- Access for 6 month(s) after purchase.
- Short Description:
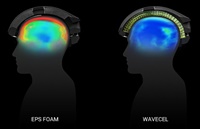
- The iconic construction hard hat, a symbol of pride for the construction worker, has changed very little in 50 years. Developments in the understanding of the causes and prevention of debilitating and often fatal head injuries is leading to a revolutionary change in the way we protect our people from head injuries on the jobsite. The classic hard hat is about to change forever. This presentation will focus on new technology available today to minimize the effects of falls and impacts to the head of the worker. We will also focus on new technologies, already in development, that can further provide protection from head injuries. Industry requirements (OSHA, ANSI) will be reviewed, and the application of worldwide standards (EN) will be discussed and applied to new helmet development and implementation.
- Price:
- $15.00 - $25.00

- Bundle:
- Fall Conference Bundle
- Presenters:
- Nate Rende
- Duration:
- 37 Minutes
- Format:
- Audio and Video
- License:
- Access for 6 month(s) after purchase.
- Short Description:
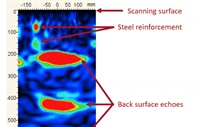
- Nondestructive testing is often used in conjunction with traditional methods to assess construction, material, or structural deficiencies in new construction. This presentation describes evaluation of unique delamination failures within below-grade, exterior walls of a new subway station. The walls were conventionally reinforced mass concrete cast against a soldier pile and lagging retention system. Shortly after construction, leakage at cracks and joints was observed and injection processes led to delamination of the interior surfaces. The assessment objectives were to determine the extent and cause of near-surface discontinuities and evaluate the structural integrity of the walls. Nondestructive testing included flaw detection using Impulse Response [structural mobility testing] and reinforcement locating using ground-penetrating radar. Sampling and petrographic examinations were conducted to correlate test results with distress conditions and evaluate the in-situ concrete.
- Price:
- $15.00 - $25.00

- Presenters:
- Nigel Parker
- Duration:
- 29 Minutes
- Format:
- Audio and Video
- License:
- Access for 6 month(s) after purchase.
- Short Description:
- The Avalon Mall parking facility is a four level above grade structure, consisting of three suspended parking levels (approximately 7,750sq.m. each) and one on-grade parking level connected to the existing mall with a new pedestrian bridge. RJC was the structural engineer of record. During construction of the parking structure extensive cracking of the suspended parking garage slabs was noted at two of the 24 pours. RJC undertook a visual assessment of the parking slabs in question to determine the extent of the noted cracking and determined over 750lin.m. of cracks ranging in size from 0.5mm to 6.5mm in width. Following the visual assessment destructive testing of the concrete was undertaken to determine its in-situ properties as well as to understand the full extent of the cracking.
- Price:
- $15.00 - $25.00
- Bundle:
- Fall Conference Bundle
- Presenters:
- Dr. Jacob L. Borgerson
- Duration:
- 24 Minutes
- Format:
- Audio and Video
- License:
- Access for 6 month(s) after purchase.
- Short Description:
- Concrete placement and finishing defects raised by a member of the project team may indicate a greater (unobserved) structural concern, a long-term durability issue, or simply an aesthetic problem. Concrete defects can delay the project schedule, require costly investigation fees, and necessitate removal and replacement. This presentation is intended to tackle concrete placement and finishing defects faced by the concrete construction industry. Topics will include: cold joints, delaminations, dusting, honeycombing, form leakage, plastic shrinkage cracking, floor flatness/levelness, in addition to others. This presentation will discuss the causes of these concrete defects, techniques for evaluating various defects, and approaches for mitigating these problems. Attendees will be introduced to various evaluation methods (e.g., impact-echo, ultrasonic pulse velocity, ground penetrating radar, concrete coring, petrographic examination, etc.) and when their use is appropriate.
- Price:
- $15.00 - $25.00
Please wait ...